Ice losses contribute to future global sea-level rise
Scientists have made significant progress in understanding the history of Antarctic melting by examining the evolving shapes of "ice bumps" on the ice shelves
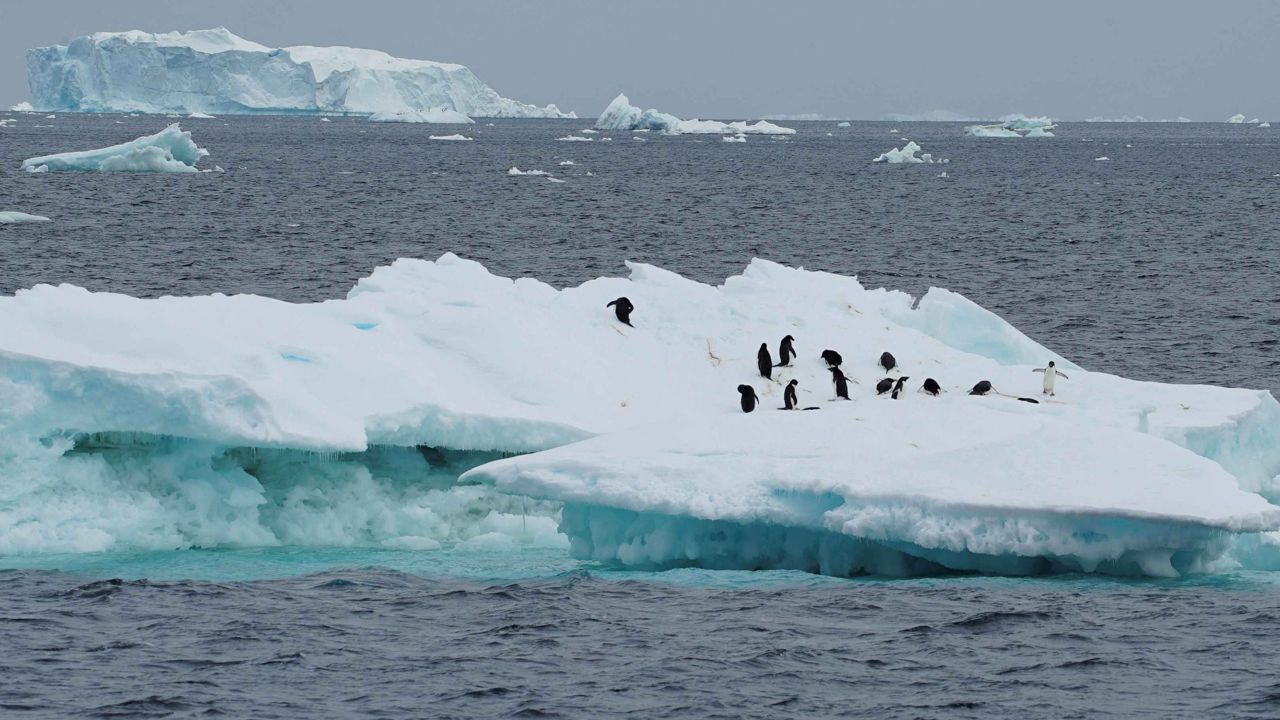

Researchers have gained valuable insights into the history of Antarctic melting by studying the changing shapes of "ice bumps" on the surface of the ice shelves.
These bumps, also known as "pinning points," are locations where glaciers are anchored to the seafloor.
The study, published in the journal Nature, revealed that more than a third of these pinning points have reduced in size since 2000, indicating an acceleration in melting.
The research focused on ice shelves, the floating fronts of glaciers that extend into the ocean, especially those west of Antarctica facing warm water and thinning.
The findings highlight the increasing contribution of Antarctic ice losses to global sea-level rise, emphasizing the importance of these ice shelves as a critical mechanism to slow down ice movement from the continent.
The study utilized satellite observations to analyze the changing shapes of the pinning points over time, providing valuable data for understanding the dynamics of Antarctic melting and its implications for future sea-level rise.
Source: Newsroom